Python For Data Science Cheat Sheet Pandas Basics Learn Python for Data Science Interactively at www.DataCamp.com Pandas DataCamp Learn Python for Data Science Interactively Series DataFrame 4 Index 7-5 3 d c b A one-dimensional labeled array a capable of holding any data type Index Columns A two-dimensional labeled data structure with columns. This cheat sheet, along with explanations, was first published on DataCamp. Click on the picture to zoom in. To view other cheat sheets (Python, R, Machine Learning, Probability, Visualizations, Deep Learning, Data Science, and so on) click here. To view a better version of the cheat sheet and read the explanations, click here. Top DSC Resources.
Pandas cheat sheet¶¶
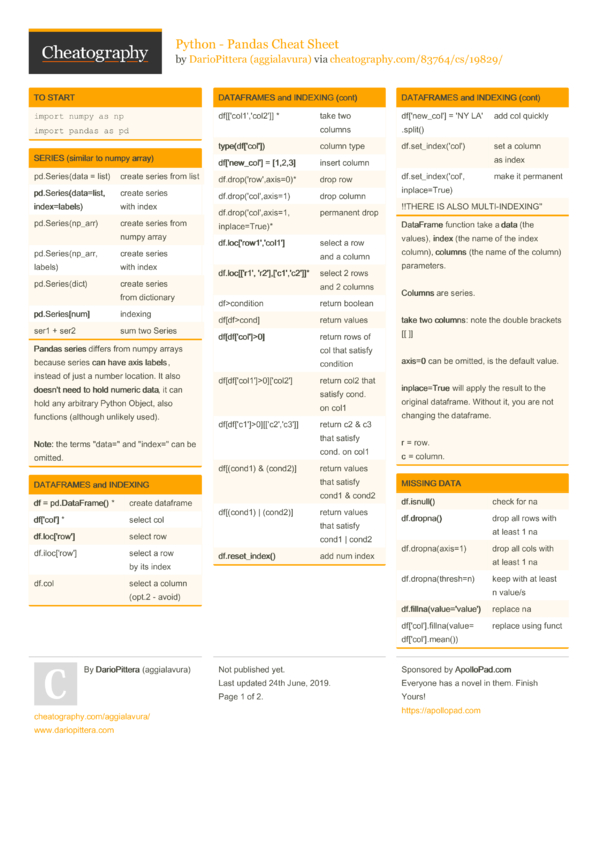
Pandas is Python Data Analysis library. Series and Dataframes are major data structures in Pandas. Pandas is built on top of NumPy arrays.
ToC
- Series
- DataFrames
- Slicing and dicing DataFrames
- Conditional selection
- Operations on DataFrames
- DataFrame index
Series¶¶
Series is 1 dimensional data structure. It is similar to numpy array, but each data point has a label in the place of an index.
Create a series¶¶
Thus Series can have different datatypes.
Operations on series¶¶
You can add, multiply and other numerical opertions on Series just like on numpy arrays.
When labels dont match, it puts a nan. Thus when two series are added, you may or may not get the same number of elements
DataFrames¶¶
Creating dataFrames¶¶
Pandas DataFrames are built on top of Series. It looks similar to a NumPy array, but has labels for both columns and rows.
| reliability | cost | competition | halflife | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car1 | 0.134302 | 0.625207 | 0.970981 | 0.717605 |
| Car2 | 0.713766 | 0.773182 | 0.059689 | 0.450899 |
| Car3 | 0.058990 | 0.904301 | 0.431487 | 0.087683 |
| Car4 | 0.509891 | 0.501037 | 0.244279 | 0.763135 |
Slicing and dicing DataFrames¶¶
Python For Data Science Cheat Sheet Pdf
You can access DataFrames similar to Series and slice it similar to NumPy arrays
Access columns¶¶
Accessing using index number¶¶
Python For Data Science Cheat Sheet
If you don’t know the labels, but know the index like in an array, use iloc and pass the index number.
Dicing DataFrames¶¶
Dicing using labels > use DataFrameObj.loc[[row_labels],[col_labels]]
| cost | competition | |
|---|---|---|
| Car2 | 0.935368 | 0.719570 |
| Car3 | 0.659950 | 0.605077 |
| cost | competition | |
|---|---|---|
| Car2 | 0.935368 | 0.719570 |
| Car3 | 0.659950 | 0.605077 |
Conditional selection¶¶
When running a condition on a DataFrame, you are returned a Bool dataframe.
| reliability | cost | competition | halflife | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car1 | 0.776415 | 0.435083 | 0.236151 | 0.169087 |
| Car2 | 0.790403 | 0.987459 | 0.370570 | 0.734146 |
| Car3 | 0.884783 | 0.233803 | 0.691639 | 0.725398 |
| Car4 | 0.693038 | 0.716824 | 0.766937 | 0.490821 |
| reliability | cost | competition | halflife | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car3 | 0.884783 | 0.233803 | 0.691639 | 0.725398 |
Chaining conditions¶¶
In a Pythonic way, you can chain conditions
Multiple conditions¶¶
You can select dataframe elements with multiple conditions. Note cannot use Python and , or. Instead use &, |
| reliability | cost | competition | halflife | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car1 | 0.776415 | 0.435083 | 0.236151 | 0.169087 |
| Car2 | 0.790403 | 0.987459 | 0.370570 | 0.734146 |
| reliability | cost | competition | halflife | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car1 | 0.776415 | 0.435083 | 0.236151 | 0.169087 |
| Car2 | 0.790403 | 0.987459 | 0.370570 | 0.734146 |
| Car3 | 0.884783 | 0.233803 | 0.691639 | 0.725398 |
Operations on DataFrames¶¶
Adding new columns¶¶
Create new columns just like adding a kvp to a dictionary.
| reliability | cost | competition | halflife | full_life | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car1 | 0.134302 | 0.625207 | 0.970981 | 0.717605 | 1.435210 |
| Car2 | 0.713766 | 0.773182 | 0.059689 | 0.450899 | 0.901799 |
| Car3 | 0.058990 | 0.904301 | 0.431487 | 0.087683 | 0.175366 |
| Car4 | 0.509891 | 0.501037 | 0.244279 | 0.763135 | 1.526270 |
Dropping rows and columns¶¶
Row labels are axis = 0 and columns are axis = 1
| reliability | cost | competition | halflife | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car1 | 0.134302 | 0.625207 | 0.970981 | 0.717605 |
| Car2 | 0.713766 | 0.773182 | 0.059689 | 0.450899 |
| Car3 | 0.058990 | 0.904301 | 0.431487 | 0.087683 |
| Car4 | 0.509891 | 0.501037 | 0.244279 | 0.763135 |
| reliability | cost | competition | halflife | full_life | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car1 | 0.134302 | 0.625207 | 0.970981 | 0.717605 | 1.435210 |
| Car2 | 0.713766 | 0.773182 | 0.059689 | 0.450899 | 0.901799 |
| Car4 | 0.509891 | 0.501037 | 0.244279 | 0.763135 | 1.526270 |
| reliability | cost | competition | halflife | full_life | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car1 | 0.134302 | 0.625207 | 0.970981 | 0.717605 | 1.43521 |
| Car4 | 0.509891 | 0.501037 | 0.244279 | 0.763135 | 1.52627 |
DataFrame Index¶¶
So far, Car1, Car2. is the index for rows. If you would like to set a different column as an index, use set_index. If you want to make index as a column rather, and use numerals for index, use reset_index
Set index¶¶
Panda Python Cheat Sheet
| reliability | cost | competition | halflife | car_names | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car1 | 0.776415 | 0.435083 | 0.236151 | 0.169087 | altima |
| Car2 | 0.790403 | 0.987459 | 0.370570 | 0.734146 | outback |
| Car3 | 0.884783 | 0.233803 | 0.691639 | 0.725398 | taurus |
| Car4 | 0.693038 | 0.716824 | 0.766937 | 0.490821 | mustang |
| reliability | cost | competition | halflife | car_names | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| car_names | |||||
| altima | 0.776415 | 0.435083 | 0.236151 | 0.169087 | altima |
| outback | 0.790403 | 0.987459 | 0.370570 | 0.734146 | outback |
| taurus | 0.884783 | 0.233803 | 0.691639 | 0.725398 | taurus |
| mustang | 0.693038 | 0.716824 | 0.766937 | 0.490821 | mustang |
| index | reliability | cost | competition | halflife | car_names | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Car1 | 0.776415 | 0.435083 | 0.236151 | 0.169087 | altima |
| 1 | Car2 | 0.790403 | 0.987459 | 0.370570 | 0.734146 | outback |
| 2 | Car3 | 0.884783 | 0.233803 | 0.691639 | 0.725398 | taurus |
| 3 | Car4 | 0.693038 | 0.716824 | 0.766937 | 0.490821 | mustang |
For working with data in python, Pandas is an essential tool you must use. This is a fast, powerful, flexible and easy to use open source data analysis and manipulation tool, built on top of the Python programming language.
But even when you’ve learned pandas in python, it’s easy to forget the specific syntax for doing something. Dbase iv tutorial. That’s why today I am giving you a cheat sheet to help you easily reference the most common pandas tasks.
It’s also a good idea to check to the official pandas documentation from time to time, even if you can find what you need in the cheat sheet. Reading documentation is a skill every data professional needs, and the documentation goes into a lot more detail than we can fit in a single sheet anyway!
Importing Data:
Use these commands to import data from a variety of different sources and formats.
Exporting Data:
Use these commands to export a DataFrame to CSV, .xlsx, SQL, or JSON. Java security unrecoverablekeyexception.
Viewing/Inspecting Data:
Use these commands to take a look at specific sections of your pandas DataFrame or Series.
Selection:
Use these commands to select a specific subset of your data.
Data Cleaning:
Use these commands to perform a variety of data cleaning tasks.
Filter, Sort, and Groupby:
Use these commands to filter, sort, and group your data.
Join/Combine:
Use these commands to combine multiple dataframes into a single one.
Statistics:
These commands perform various statistical tests. (They can be applied to a series as well)
I hope this cheat sheet will be useful to you no matter you are new to python who is learning python for data science or a data professional. Happy Programming.
You can alsodownload the printable PDF file from here.
.